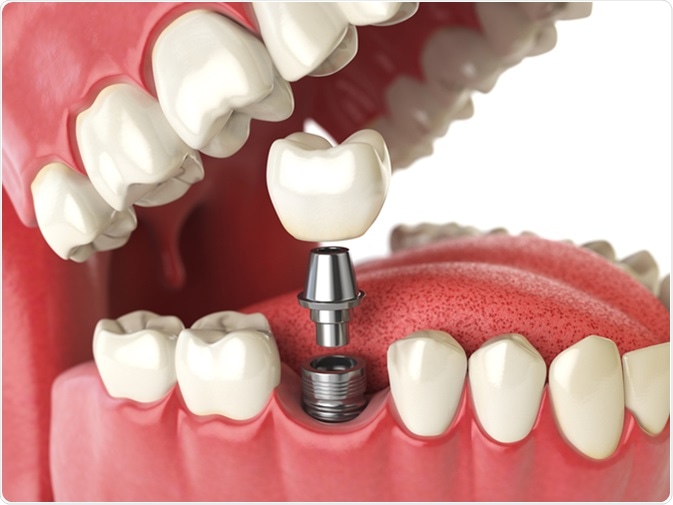
Dental implants —artificial replacement for natural teeth/roots — are an alternative to partial and complete dentures or bridges. The implant, which acts as a tooth, offers more stability and comfort than the dentures. Implants can restore the ability to chew food and improve facial appearance and speech.
How are implants placed?
Implant surgery is performed in a dentist’s office, in a three-step process:
A dentist surgically places an implant in the jawbone directly, like a natural root of the tooth. The implant will usually remain covered for three to six months after this initial surgery, allowing the bone to develop around the implant to help hold it in place.
When this waiting period is over, the dentist will uncover the implant and attach an extension to the implant, called a post.
In the third and final step, once healing is completed, the implant can serve as a foundation for the new tooth. The dentist then makes a crown (or other artificial tooth replacement) and attaches it to the implant post.